Core Concepts
Below are the description to the main terms and concepts used in agenta.
Templates
Templates are the workflows used by LLM-powered applications. Agenta comes with two default templates:
- Completion Application Template: For single-prompt applications that generate text completions.
- Chat Application Template: For applications that handle conversational interactions.
Agenta also allows you to create custom templates for your workflows using our SDK. Examples include:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Applications
- Chains of Multiple Prompts
- Agents Interacting with External APIs
After creating a template, you can interact with it in the playground, run no-code evaluations, and deploy versions all from the web UI.
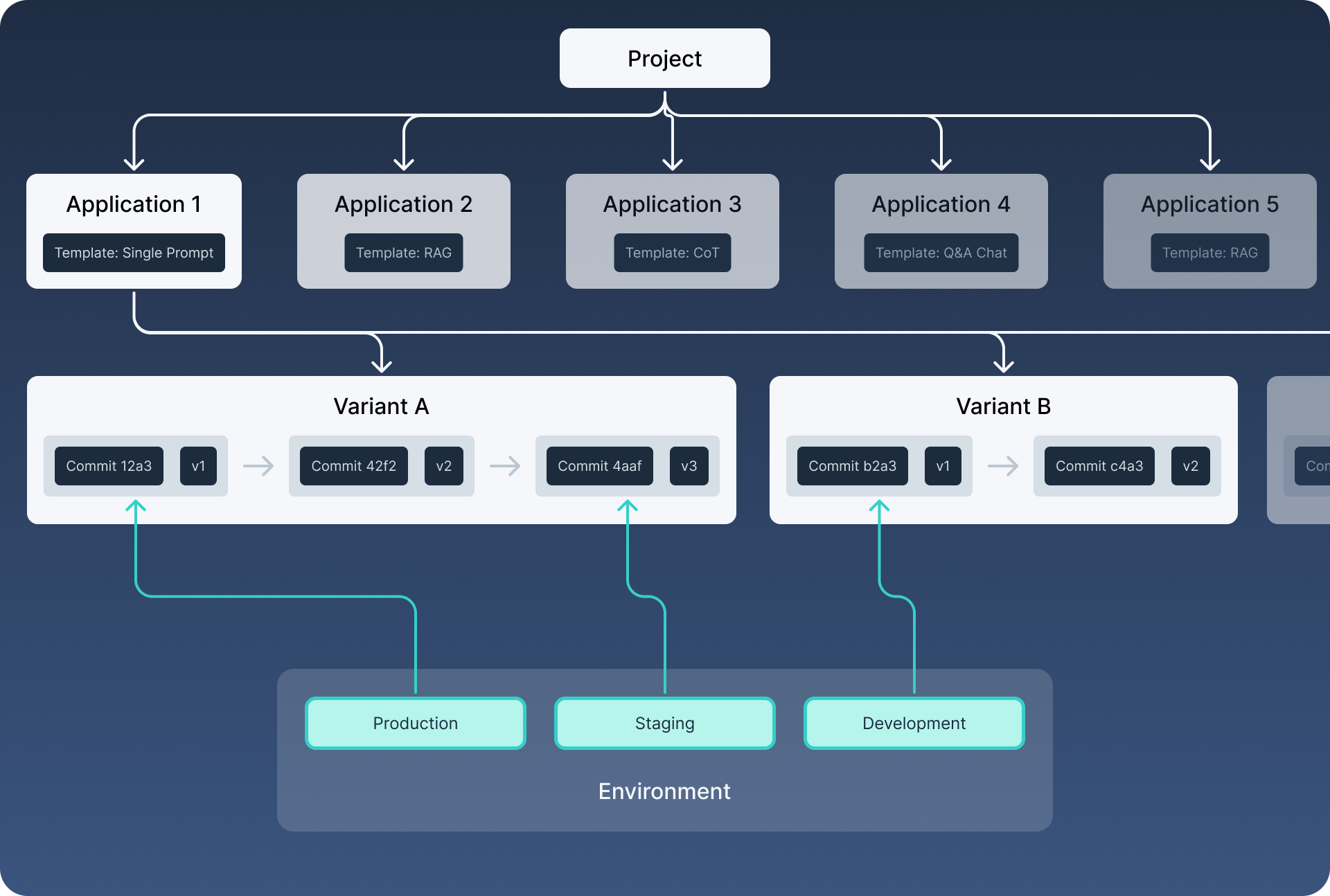
Applications
An application uses a template to solve a specific use case. For instance, an application could use the single-prompt template for tasks like:
- Tweet Generation: Crafting engaging tweets based on input topics.
- Article Summarization: Condensing long articles into key points.
Variants
Within each application, you can create variants. Variants are different configurations of the application, allowing you to experiment with and compare multiple approaches. For example, for the "tweet generation" application, you might create variants that:
- Use different prompt phrasings.
- Adjust model parameters like temperature or maximum tokens.
- Incorporate different styles or tones (e.g., professional vs. casual).
Versions
Every variant is versioned and immutable. When you make changes to a variant, a new version is created. Each version has a commit id that uniquely identifies it.
Environments
Environments are the interfaces where your deployed variants are accessible. You can deploy a version of a variant to an environment. Each environment has a user-defined environment name (e.g. development, staging, production) that specifies its context or stage.
You can then integrate the environment into your codebase to fetch the configuration deployed on that environment. Additionally, you can directly invoke the endpoints relating to the environment containing the application running with that configuration.
By default, applications come with three predefined environments:
- Development: For initial testing and experimentation.
- Staging: For pre-production testing and quality assurance.
- Production: For live use with real users.
When deploying a variant to an environment, the latest version of that variant gets deployed. Each environment points to a specific version of a variant (a certain commit). Updating the variant after deploying does not automatically update the environment.